If you’re looking to reduce your energy bills, make your home more comfortable, and minimize your environmental impact, conducting a DIY home energy audit is a great first step. A home energy audit helps identify areas of energy waste and provides insights into how to improve energy efficiency. In this guide, we’ll explore where to start with a DIY home energy audit, helping you pinpoint opportunities for energy savings.
1. Understand Your Utility Bills
Begin by understanding your utility bills. Analyze your energy and water bills to identify patterns and trends. Look for any spikes in usage during specific months or seasons. Understanding your consumption patterns provides a baseline for assessing the effectiveness of your energy-saving efforts later on.
2. Locate Air Leaks
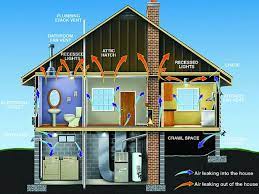
Air leaks are a significant source of energy waste. Start by inspecting windows, doors, and exterior walls for drafts. Hold a lit incense stick near potential leak areas and observe the smoke movement. Common places for air leaks include window frames, door frames, electrical outlets, and gaps in walls. Seal these leaks with weatherstripping, caulk, or expanding foam.
3. Inspect Insulation
Proper insulation is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. Check the insulation levels in your attic, walls, and floors. Inadequate insulation can lead to heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Consider adding insulation where needed, and replace or reinforce existing insulation for optimal efficiency.
4. Evaluate Heating and Cooling Systems
Heating and cooling systems account for a significant portion of energy usage. Check your HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) system’s filters and replace them regularly to ensure efficiency. Examine ductwork for leaks and seal any gaps. Consider upgrading to a programmable thermostat for better temperature control and energy savings.
5. Assess Lighting Efficiency
Lighting plays a role in your home’s energy consumption. Replace incandescent bulbs with energy-efficient LED or CFL bulbs. Consider installing dimmer switches and motion sensors to control lighting usage. Assess natural lighting opportunities and maximize the use of daylight to reduce reliance on artificial lighting during the day.
6. Examine Appliances and Electronics
Appliances and electronics contribute to your home’s energy consumption. Evaluate the energy efficiency of your appliances, and consider upgrading to Energy Star-rated models. Unplug electronic devices when not in use, as they may still draw power in standby mode. Use power strips to easily disconnect multiple devices at once.
7. Check Water Heating Efficiency
Water heating is a significant energy expense. Inspect your water heater for leaks and set the temperature to a recommended 120 degrees Fahrenheit (49 degrees Celsius). Consider insulating your water heater and hot water pipes to minimize heat loss. If your water heater is old or inefficient, upgrading to a newer, more energy-efficient model can lead to substantial savings.
8. Review Windows and Doors
Windows and doors can contribute to heat gain or loss. Inspect them for proper sealing and weatherstripping. Upgrade to energy-efficient windows or add window films to improve insulation. Consider using thermal curtains or blinds to further enhance energy efficiency by blocking heat transfer.
9. Assess Energy Usage Habits
Your daily habits also play a role in your home’s energy efficiency. Evaluate how and when you use energy. Simple changes, such as turning off lights when leaving a room, using energy-efficient appliances, and washing clothes in cold water, can contribute to overall energy savings.
10. Consider Renewable Energy Options
If feasible, explore renewable energy options for your home. Solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems can supplement or replace traditional energy sources. Research available incentives, rebates, and financing options to make renewable energy systems more affordable.
11. Use DIY Home Energy Audit Tools
Take advantage of online tools and resources designed for DIY home energy audits. Some websites offer interactive quizzes and checklists to guide you through the audit process. These tools can help you identify specific areas of improvement and prioritize energy-saving projects.
12. Create an Action Plan
Based on your findings, create an action plan for improving energy efficiency in your home. Prioritize projects based on their impact and feasibility. Set realistic goals and a timeline for implementing changes. Consider seeking professional assistance for more complex projects, such as HVAC system upgrades or insulation installations.
By starting with these steps, you can lay the groundwork for a comprehensive DIY home energy audit. Identifying and addressing energy inefficiencies not only reduces your environmental footprint but also leads to long-term cost savings and a more comfortable living space. Embark on your DIY energy audit journey, and enjoy the benefits of a more energy-efficient home.