Introduction
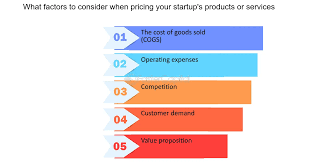
Pricing is a critical aspect of business strategy, impacting revenue, market positioning, and customer perception. Determining the right pricing strategy requires a careful balance between covering costs, staying competitive, and delivering value to customers. This article explores various strategies for pricing products and services to optimize profitability and market success.
Cost-Plus Pricing: Setting a Baseline
Cost-plus pricing involves calculating the cost of production or service delivery and adding a predetermined profit margin. This straightforward approach ensures that all costs are covered, providing a baseline for pricing. While simple, businesses must be cautious not to underprice or overprice based solely on costs, as it may not reflect market demand or perceived value.
Value-Based Pricing: Aligning with Customer Value
Value-based pricing focuses on the perceived value of a product or service to the customer. It involves understanding what customers are willing to pay based on the benefits and value they receive. By aligning pricing with the perceived value, businesses can capture a share of the value they deliver, even if costs are lower than the selling price.
Competitive Pricing: Staying in the Game
Competitive pricing involves setting prices based on what competitors are charging for similar products or services. This strategy aims to stay competitive in the market and may involve pricing products slightly lower, higher, or at par with competitors. Regular market analysis is crucial to adjust pricing in response to changes in the competitive landscape.
Penetration Pricing: Capturing Market Share
Penetration pricing involves setting initial prices lower than the perceived market value to gain quick market share. This strategy is often used for new product launches. Once a significant market share is captured, prices may be adjusted upward. It’s essential to have a clear plan for transitioning to regular pricing to avoid long-term profitability challenges.
Skimming Pricing: Maximizing Early Adopters
Contrary to penetration pricing, skimming pricing involves setting high initial prices to maximize revenue from early adopters or those willing to pay a premium for innovation. Over time, prices may be gradually lowered to attract a broader customer base. This strategy is common in industries where rapid technological advancements lead to premium pricing for cutting-edge products.
Dynamic Pricing: Flexibility for Market Changes
Dynamic pricing involves adjusting prices in real-time based on market demand, competitor pricing, or other external factors. This strategy is common in e-commerce, travel, and other industries where pricing conditions can change rapidly. Automated algorithms and data analysis play a crucial role in implementing dynamic pricing effectively.
Bundle Pricing: Offering Value Packages
Bundle pricing involves grouping several products or services together and offering them at a discounted rate compared to purchasing each item individually. This strategy encourages customers to buy more, increasing the overall transaction value. Businesses must carefully structure bundles to provide perceived value and drive sales.
Geographic Pricing: Adapting to Regional Differences
Geographic pricing recognizes regional variations in purchasing power and market conditions. It involves adjusting prices based on factors such as local competition, cost of living, and currency exchange rates. This strategy allows businesses to remain competitive and attractive in diverse markets.
Conclusion
Choosing the right pricing strategy is a complex decision that requires a deep understanding of the market, customer behavior, and business objectives. By aligning pricing with value, staying competitive, and adapting to market dynamics.