The Science of Customer Feedback Management
In the digital age, where customer experiences can make or break a business, the science of customer feedback management has become a strategic imperative. Effective feedback management goes beyond collecting opinions; it involves a systematic and data-driven approach to understanding customer sentiments and leveraging insights for continuous improvement. Let’s delve into the intricacies of the science behind customer feedback management and how businesses can harness its power.
1. Understanding the Value of Customer Feedback
The science of customer feedback management begins with recognizing the inherent value of customer opinions. Feedback is a direct source of insights into customer satisfaction, pain points, and expectations. Businesses that understand the significance of this input can leverage it to enhance products, services, and overall customer experiences.
2. Strategic Collection of Feedback Data
Collecting feedback strategically is a key component of effective feedback management. Businesses utilize various channels, including surveys, social media, and direct interactions, to gather customer input. The science lies in selecting the right channels, employing diverse methods, and timing the requests for feedback to capture authentic and timely insights.
3. Implementing Advanced Feedback Analytics
Once feedback data is collected, the science moves to the realm of analytics. Advanced analytics tools enable businesses to sift through large datasets, identify patterns, and extract meaningful insights. Sentiment analysis, for example, helps gauge the emotional tone of customer feedback, providing a nuanced understanding of customer perceptions.
4. Categorizing and Prioritizing Feedback Themes
The science of customer feedback management involves categorizing feedback into themes to identify recurring issues or positive aspects. By prioritizing these themes based on their impact on customer satisfaction and business objectives, organizations can focus on addressing the most critical areas for improvement or enhancement.
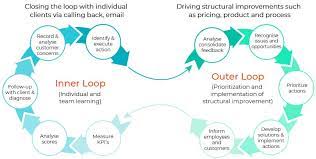
5. Closed-loop Feedback Systems
Closed-loop feedback systems are integral to the science of customer feedback management. These systems involve responding to customers promptly after receiving feedback, acknowledging their input, and outlining actions taken or planned to address concerns. This proactive approach not only demonstrates attentiveness but also fosters a sense of customer-centricity.
6. Integration with Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
To maximize the impact of customer feedback, businesses integrate feedback management with CRM systems. This integration ensures that customer feedback is seamlessly linked with customer profiles, enabling a holistic view of individual customer experiences. The interconnected data provides a comprehensive understanding of the customer journey.
7. Continuous Feedback Iteration
Feedback management is not a one-time endeavor; it’s an iterative process. The science involves establishing mechanisms for continuous feedback collection, analysis, and action. This iterative approach allows businesses to adapt to evolving customer preferences, address emerging issues, and consistently enhance their offerings.
8. Employee Training and Feedback Handling
Equipping employees to handle and act upon customer feedback is a vital aspect of feedback management. The science involves training frontline staff to interpret feedback, respond empathetically, and take appropriate actions. Well-trained employees play a crucial role in turning customer feedback into tangible improvements.
9. Feedback-driven Innovation
Beyond addressing concerns, the science of customer feedback management extends to driving innovation. Businesses use customer insights to identify new opportunities, refine existing products or services, and stay ahead of market trends. Customer feedback becomes a catalyst for continuous innovation and differentiation.
10. Creating a Customer-Centric Culture
The overarching science of customer feedback management is about cultivating a customer-centric culture within an organization. It involves instilling a mindset where every employee values and seeks customer input. A customer-centric culture ensures that feedback is not just a process but a guiding principle in decision-making and business strategy.
Conclusion
The science of customer feedback management is a multidimensional and evolving discipline that empowers businesses to understand, adapt, and excel in the ever-changing landscape of customer expectations. By strategically collecting, analyzing, and acting upon customer feedback, organizations not only enhance customer satisfaction but also position themselves for sustained success in a competitive marketplace. As businesses embrace the science behind customer feedback management, they embark on a journey of continual improvement and customer-centric innovation.